Table of Contents
Windows Information
SSH on Windows
You can use the program SecureCRT to connect to Unix and Linux systems using SSH. SSH should always be used instead of telnet - in fact most of our servers now have telnet switched off.
To run SecureCRT, either double-click on the SecureCRT icon on the desktop, or choose it from the Programs section of the Start Menu.
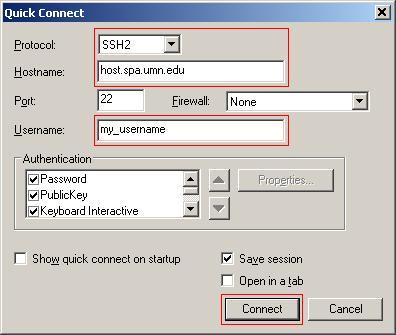
Quick Connect
Bring up the SecureCRT Quick Connect window (shown below) from the File menu. Set the Protocol field to ssh2 (ssh1 is not recommended), and enter the hostname of the server you wish to connect to, and your username.
Click Connect to start your connection to the remote host.
The first time you connect to a particular host using ssh, you will receive a message about accepting a new host key. In general you should choose the Accept & Save option.
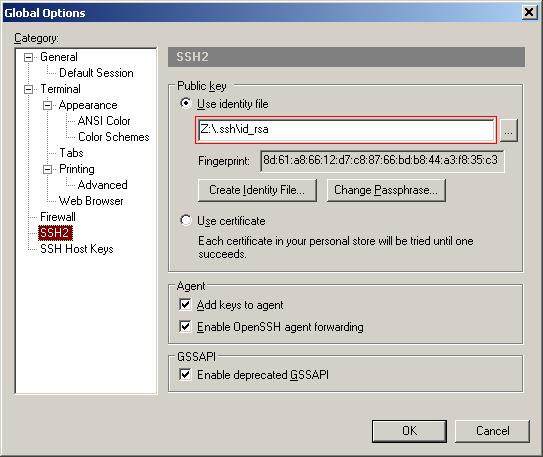
Key Authentication
Click on Global settings… from the Options menu. In the dialog that appears select the SSH2 category and ensure that Use identity file is selected. Enter Z:\.ssh\id_rsa into the text box underneath it and click Ok.
Using Sessions
When connecting multiple times to the same host, it is often useful to create a “session”. Sessions store the information used to connect to a host and allow you to easily connect later. A session can be created while using Quick Connect by checking the Save Session box. Saved sessions display by default when SecureCRT is first opened, but can also be found by opening the File menu and clicking on Connect.
X Windows Forwarding
To use X windows applications on the remote host, you should switch on X11 forwarding. This lets SSH set up a secure, encrypted connection for displaying your X windows. To enable X windows forwarding you must be using sessions.
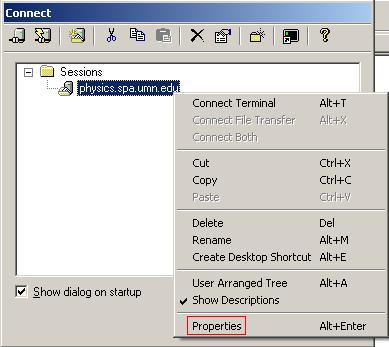
You can enable forwarding on a session through the Connect window:
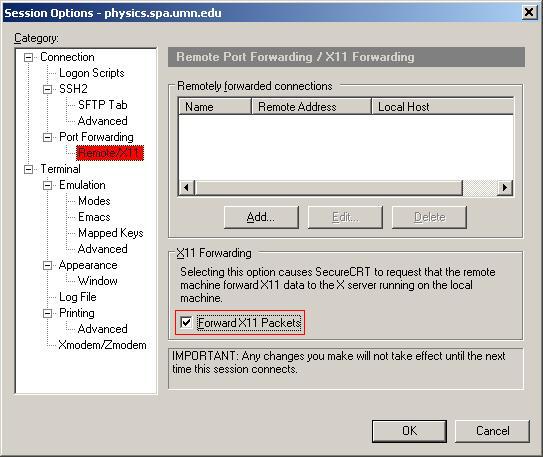
Right click on the desired session and select Properties. Click on the Remote/X11 category and select Forward X11 Packets.
More information on using X11 with SSH is given on the Xming page.